Understanding Poodle Hair Layers: Cuticle, Cortex, and Medulla
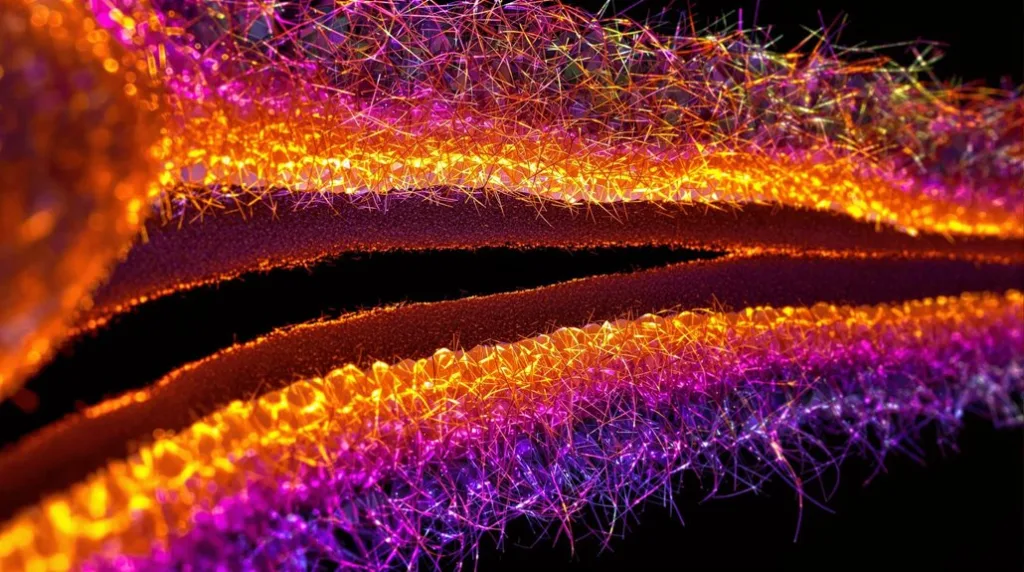
Your Poodle’s distinctive curly coat has three specialized layers working together like a sophisticated biological fabric. The outermost cuticle layer acts as a protective barrier, controlling moisture and creating shine. The middle cortex layer makes up 75% of the hair shaft, providing strength through keratin proteins and housing color-giving melanin. The innermost medulla layer offers insulation through air-filled spaces, typically showing an interrupted pattern. When you understand how these layers function together, you’ll be better equipped to maintain your Poodle’s signature coat in ideal condition.
Key Takeaways
- Poodle hair consists of three distinct layers: the protective outer cuticle, the strong middle cortex, and the insulating inner medulla.
- The cuticle’s scale-like structure protects the hair shaft and controls moisture, contributing to the coat’s shine and smoothness.
- The cortex makes up 75% of the hair shaft, containing keratin proteins for strength and melanin granules for color.
- The medulla measures 35 micrometers in diameter and features air-filled spaces that provide thermal insulation for poodles.
- Regular grooming and proper nutrition maintain the health of all three layers, preventing damage and supporting optimal coat appearance.
The Three Essential Hair Layers
When you look at a Poodle’s distinctive coat, you’re actually seeing three essential layers working together to create that luxurious texture. Each layer serves a specific purpose in maintaining your Poodle’s healthy, resilient coat.
The cortex, which forms the bulk of the hair shaft, contains keratin proteins that give your Poodle’s hair its strength and elasticity. This middle layer also houses the melanin pigments responsible for your dog’s coat color.
Meanwhile, the innermost layer, called the medulla, isn’t always present in every hair strand but provides additional insulation when it is. The protective cuticle layer on the outside acts like armor for the inner structures.
The way these layers interact directly impacts your Poodle’s coat health. Hair layer interactions contribute to moisture retention throughout the shaft, preventing dryness and maintaining flexibility.
When all three layers function properly together, they create a strong, healthy coat that’s resistant to damage. You’ll notice this harmony in your Poodle’s coat through its shine, texture, and overall appearance.
Understanding these layers helps you provide better care for your dog, as each grooming decision you make affects all three components of the hair structure.
Cuticle Layer Structure and Function
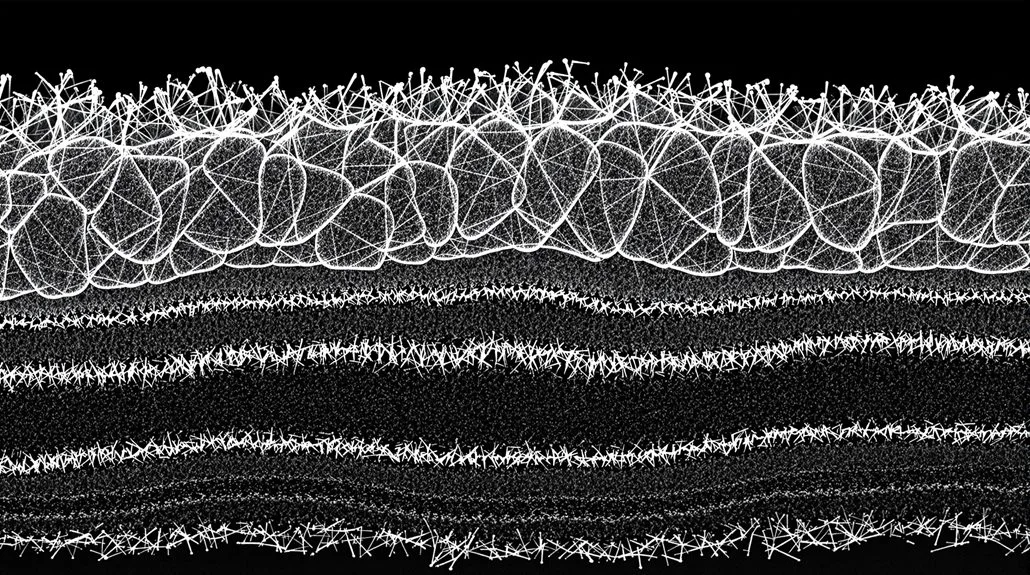
As the outermost layer of your Poodle’s hair shaft, the cuticle plays an important protective role through its unique scale-like structure. These transparent scales always point from the root to the tip of the hair, creating a protective barrier that safeguards the inner layers of your dog’s coat.
When your Poodle’s cuticle health is ideal, you’ll notice a natural shine and smooth texture to their coat. Regular monitoring helps prevent issues with coat health.
Your Poodle’s cuticle diversity is influenced by genetics and environmental factors, affecting both texture and appearance. The integumentary system works together with the cuticle to protect underlying tissues and organs.
Under a microscope, you’ll find distinct mosaic patterns typical of dog hair. Understanding these patterns helps you better care for your Poodle’s coat, as cuticle damage can occur from heat styling, harsh grooming practices, or environmental stress.
When the cuticle becomes compromised, you’ll notice a dull, lifeless appearance to your dog’s coat.
Regular maintenance is vital for cuticle repair and preservation. You can maintain your Poodle’s cuticle shine by keeping their coat clean and properly conditioned.
Remember that factors like nutrition, illness, and stress can impact the cuticle’s condition, directly affecting your Poodle’s overall coat health and appearance.
Cortex Layer Properties
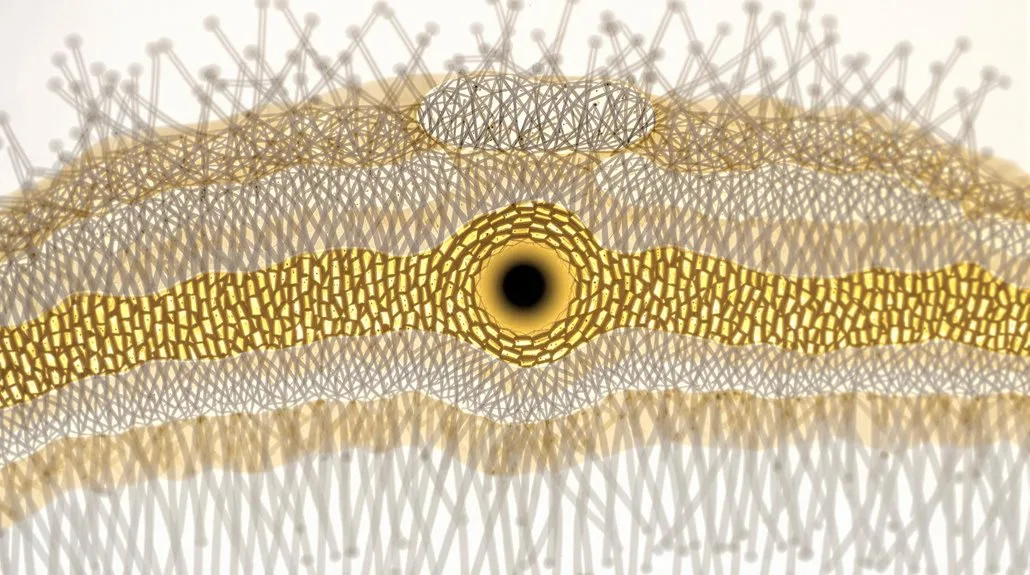
The cortex layer forms the largest portion of your Poodle’s hair shaft, consisting primarily of keratin-rich, elongated cells. These spindle-shaped cells contribute considerably to your dog’s hair strength and cortex elasticity, allowing the hair to stretch and return to its original shape.
Within the cortex, you’ll find pigment granules that determine your Poodle’s distinctive coat color through the distribution of melanin.
The structure of your Poodle’s cortex can vary based on genetics and environmental factors, with cortex diameters typically ranging from 2.2 to 4.4 micrometers.
The pigment distribution within the cortex affects not only the color but also how light interacts with the hair, influencing its overall appearance and shine.
You’ll notice that proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining the health of this important layer. Using a polarising microscope can enhance visibility when examining the cortex structure in detail.
When examining your Poodle’s hair under a microscope, you’d observe that the cortex contains small air spaces called cortical fusi and ovoid bodies. These structural elements, combined with the arrangement of keratin proteins, contribute to your Poodle’s characteristic coat texture and mechanical properties.
Medulla Layer Characteristics

Inside your Poodle’s hair shaft, a distinct medulla layer forms the innermost core, featuring unique patterns and dimensions that set it apart from other breeds. Your Poodle’s medulla typically displays an interrupted pattern and boasts one of the largest medulla dimensions among dog breeds, measuring approximately 35.00 μm in diameter.
When examining medulla types in your Poodle’s hair, you’ll find they can be continuous, fragmental, or ladder-shaped, though the interrupted pattern is most common. The medulla’s significance extends beyond basic structure, as it provides vital thermal insulation through its air-filled compartments and helps distinguish your Poodle’s hair from other breeds in forensic analysis.
Three key characteristics make your Poodle’s medulla layer unique:
- Larger diameter (35.00 μm) compared to breeds like Golden Retrievers (4.4 μm)
- Distinctive interrupted medulla pattern that’s consistent across Poodles
- Well-defined air spaces that enhance insulation properties
Understanding your Poodle’s medulla patterns and dimensions isn’t just fascinating – it’s essential for breed identification and helps explain why Poodle hair provides such effective insulation against various weather conditions.
Hair Growth Cycle

While your Poodle’s coat maintains its distinctive appearance, a complex growth cycle controls each hair’s development through four distinct phases. Understanding these phases helps you better manage your Poodle’s hair types and growth patterns. Poor nutrition can disrupt this natural cycle.
During the anagen phase, which lasts 3-5 years, your Poodle’s hair actively grows about 1-1.5 cm monthly. This phase represents 90% of the hair growth cycle, allowing the coat to reach its full potential length. Hair grows faster in summer months.
The catagen phase follows, lasting 1-2 weeks, where the hair stops growing and disconnects from its blood supply. The follicle’s diameter decreases by about one-sixth during this change.
Next comes the telogen phase, a 3-4 month resting period where 10-15% of your Poodle’s hairs remain dormant in their follicles.
Finally, the exogen phase marks the natural shedding process, where old hairs detach to make way for new growth. Your Poodle typically sheds 50-100 telogen hairs daily during this phase.
This continuous cycle guarantees your Poodle’s coat remains healthy and maintains its characteristic texture and appearance year-round.
Protective Properties of Hair Layers
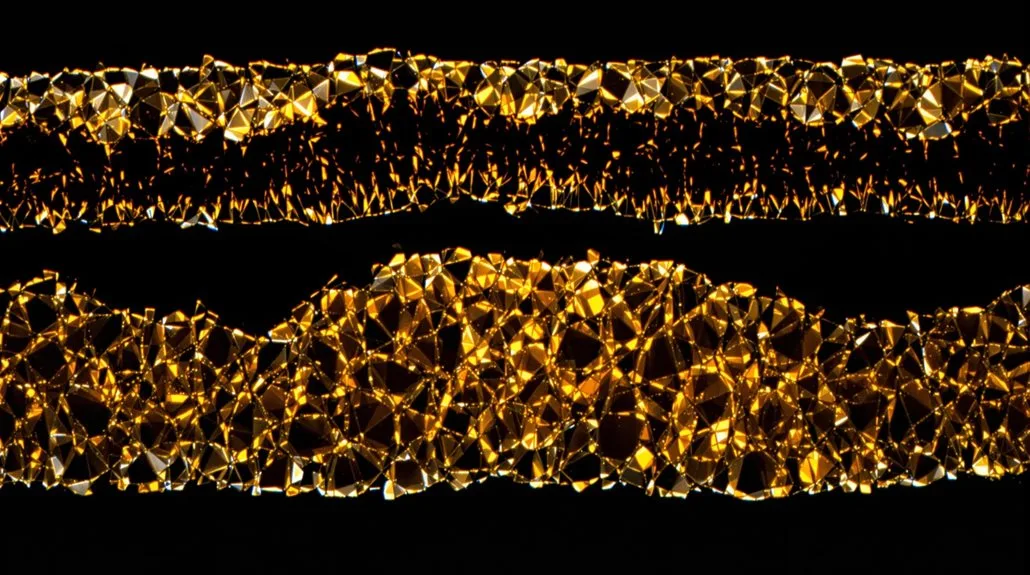
Each Poodle hair contains three distinct protective layers working together to maintain coat health and resilience.
Your Poodle’s hair starts with the cuticle, an outer shield of overlapping cells that prevents cuticle damage and acts as a protective barrier against environmental stress. This layer’s direction, pointing away from the scalp, helps control moisture retention while maintaining structural integrity.
Regular brushing and harsh chemical treatments can cause physical cuticle erosion over time. If you find your Poodle’s coat health declining, it could be due to outdated grooming techniques that need updating.
The cortex, making up about 75% of each hair strand, provides cortex strength through tightly packed keratin bundles. It’s responsible for:
- Determining your Poodle’s coat texture and wave pattern
- Housing melanin granules that give your dog’s coat its color
- Providing essential strength through disulfide bonds
At the core, you’ll find the medulla, though its medulla function isn’t fully understood. This innermost layer features high hair porosity due to its air-filled cavities and can vary considerably between different hair strands.
Layer interaction between these three components is vital – when the cuticle’s damaged, it can’t protect the cortex effectively, leading to weakened hair structure. That’s why maintaining the health of all three layers is important for your Poodle’s coat quality.
Poodle Hair Maintenance

Proper maintenance of your Poodle’s hair demands a thorough understanding of its unique structure and care requirements.
By focusing on essential grooming techniques that protect all three hair layers – cuticle, cortex, and medulla – you’ll help maintain your dog’s coat health and appearance.
Start with gentle brushing to prevent tangles while protecting the cuticle’s overlapping scales. When washing your Poodle, use appropriate shampoos and guarantee thorough rinsing to avoid residue that can lift the cuticle layers.
During drying, minimize heat exposure to prevent moisture loss and cuticle damage, which can affect the cortex and medulla beneath. Your Poodle’s hair health also depends greatly on nutritional support. A balanced diet guarantees proper hair growth and maintenance of all three layers.
Watch for signs of healthy hair, including a natural shine from well-sealed cuticles, smooth texture, and consistent growth patterns. Regular grooming sessions allow you to monitor these indicators while addressing potential issues before they worsen.
When you notice changes in texture, shine, or growth rate, adjust your maintenance routine or consult a professional groomer for guidance.
Common Hair Layer Problems
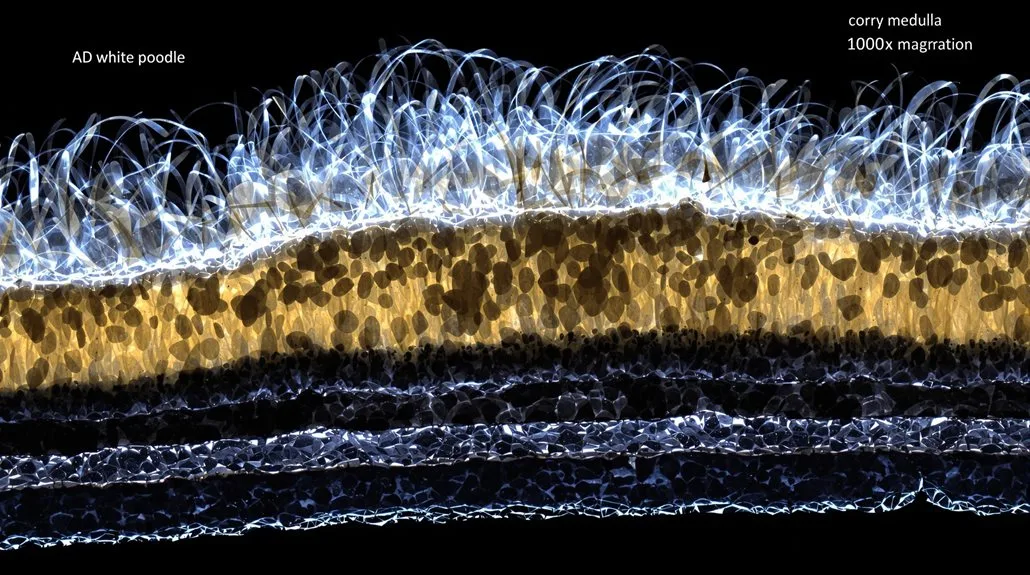
Despite their resilient nature, Poodle hair layers can develop various problems that affect coat health and appearance. You’ll notice these issues primarily manifest in three distinct layers:
- Cuticle damage from excessive grooming techniques
- Cortex deterioration due to chemical processing
- Medulla irregularities affecting overall hair structure
When your Poodle’s cuticle layer becomes compromised, you’ll see increased tangles, matting, and a dull appearance. Proper hair care is essential, as open cuticles can’t protect the inner layers effectively.
The cortex layer, which provides strength and elasticity, suffers when exposed to harsh chemicals or heat styling tools, leading to brittleness and breakage.
Your Poodle’s medulla layer, typically larger than in human hair, can become fragmented or inconsistent. This affects the coat’s texture and overall health. Poor nutrition and improper grooming techniques often contribute to these problems across all layers.
You’ll need to watch for signs like excessive shedding, which often indicates underlying layer issues. Maintaining proper moisture balance and using gentle grooming methods will help preserve the integrity of all three hair layers.
Genetics and Hair Structure

The complex structure of your Poodle’s coat stems directly from their genetic blueprint. Your Poodle’s unique hair characteristics, from the shape of each strand to its texture and color, are all determined by specific genetic factors.
The shape of your dog’s hair follicles plays an essential role – round follicles create straight hair, while oval or irregular ones produce the characteristic curls that Poodles are known for.
When you look at your Poodle’s coat, you’ll notice its distinctive texture, which is also a result of genetic variation. These genes influence how the three main layers of each hair – the cuticle, cortex, and medulla – develop and interact.
The cuticle’s overlapping scales, the cortex’s melanin content, and the medulla’s pattern are all inherited traits. The distribution of melanin in the cortex determines your Poodle’s coat color, while the arrangement of keratin proteins affects hair strength and texture.
Your Poodle’s species-specific hair characteristics, including the type of medulla and the pattern of cuticle scales, are all coded in their DNA, making each Poodle’s coat uniquely their own while maintaining breed-specific traits.
Hair Health Assessment
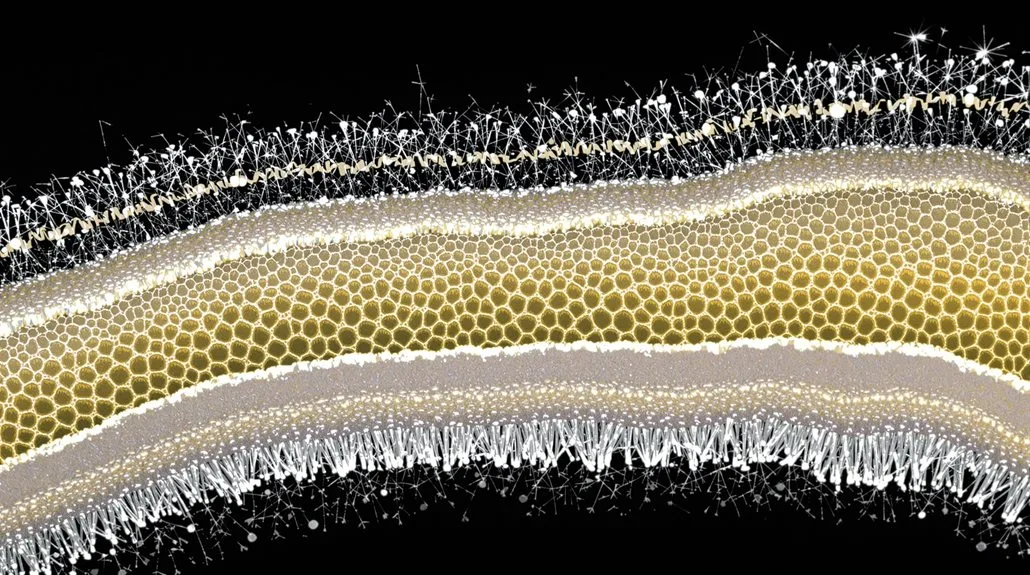
Regularly reviewing your Poodle’s hair health requires understanding the three key layers of their coat structure. When evaluating your dog’s hair health, you’ll need to examine signs from each layer to guarantee ideal condition and identify potential issues early on.
Here are three critical hair assessment techniques you should implement:
- Examine the cuticle layer by running your fingers along the hair shaft – if it feels rough or catches easily, the protective scales may be damaged.
- Check the cortex health by testing the hair’s elasticity – healthy strands should stretch slightly and return to their original shape.
- Monitor overall shine and texture, which reflect the combined health of all layers, including the medulla.
For maximum hair health benefits, you’ll want to maintain regular grooming practices that protect the cuticle layer while supporting the cortex structure.
Pay attention to your Poodle’s natural oil distribution, as these oils help seal the cuticle and maintain shine. If you notice changes in texture, excessive shedding, or loss of curl pattern, it might indicate underlying health issues affecting one or more hair layers.
Conclusion
You’ve learned about the three critical layers of your Poodle’s hair and how they work together. Remember that proper maintenance of the cuticle protects the cortex and medulla beneath. By understanding these layers, you’ll make better grooming choices and spot potential issues early. Keep monitoring your Poodle’s coat health, and don’t forget that genetics play a key role in your pet’s unique hair structure.






